Product:
Interacting with WebViewer events
This guide will go over the order of events that happen when WebViewer is instantiated and a document is loaded.
Here is a complete visualization of the order of events that occur. For a more detailed description, see the sections below.
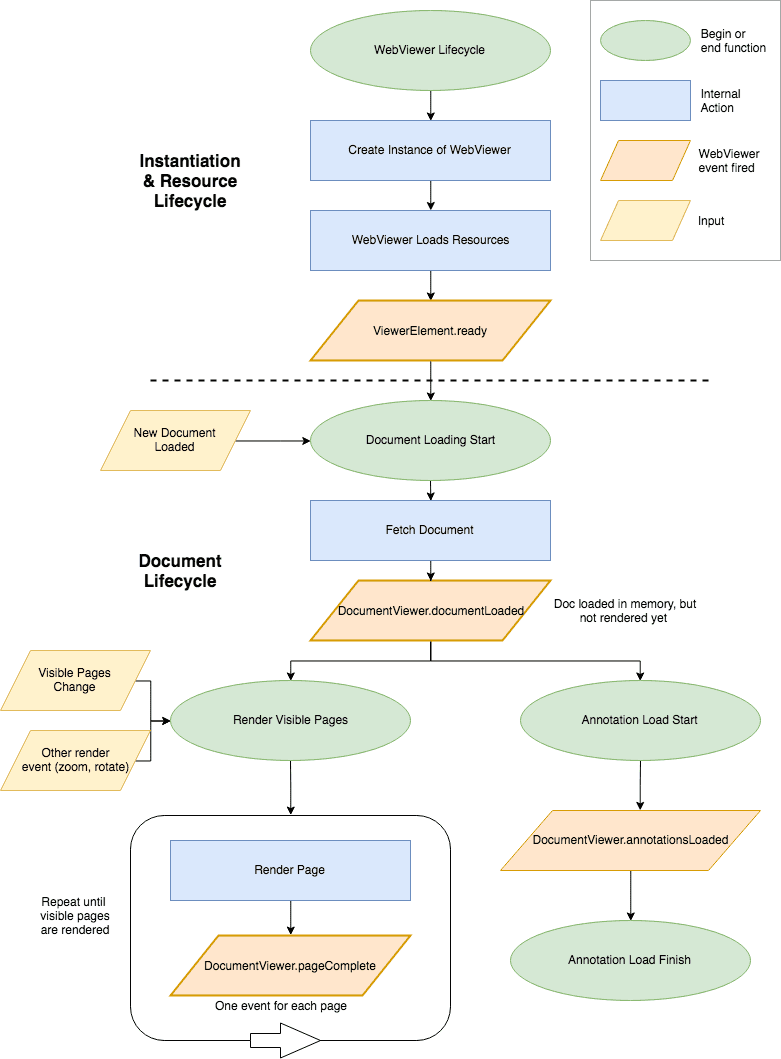
Instantiation and Resource Loading
The first step you take when implementing WebViewer is creating a new instance of WebViewer. This is done with the PDFTron.WebViewer constructor, like so:
JavaScript
WebViewer then creates an iframe in the DOM element that you provide, and starts loading all the necessary resources in that iframe, including the UI and web workers.
When those resources are finished loading and WebViewer can be interacted with, the WebViewer promise resolves.
WebViewer promise
Once the WebViewer promise resolves, you can begin to interact with WebViewer. This includes UI customizations, loading documents, subscribing to other WebViewer events, and any other functionality you may want to use.
Keep in mind that at this point, the document (if one was provided) has not been loaded and cannot be interacted with yet. See document loading for more info.
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Document Loading
Once all the required WebViewer resources are loaded, documents can start loading. You can load a document either by passing one to the initialDoc constructor option, or calling loadDocument after the WebViewer promise resolves (as seen above).
The first step of loading a document is loading all, or part, of the document into memory. Once we have enough information about the document stored in memory, the first document lifecycle event is called, DocumentViewer.documentLoaded.
DocumentViewer.documentLoaded
This event is called when the document is loaded into memory and you can start interacting with the document. This includes page manipulation, loading annotations, initializing collaboration, and more!
You can bind to the event like so:
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Keep in mind that this callback gets fired for every document that gets loaded throughout the life of your app. If you want the callback to only be fired once, you can unsubscribe from the event like so:
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Document Load Error Handling
On the other hand, if a document fails to load, a loaderror event will be triggered on the iframe window. Although WebViewer can recover from most loading errors, you may want to show a custom error message, submit a log to an API, and/or load a new document.
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Document and Annotation Rendering
After the document is in memory, we are ready to start rendering to the screen. The document and its annotations are rendered in parallel, and there are two main events that are fired during this cycle.
DocumentViewer.pageComplete
This event is fired for each page that is rendered. We only render the pages that are visible on the screen, so this event won't get fired for every page in the document at once. This event will get called when the user scrolls up and down the document, or when a page is zoomed or rotated, or anything else that makes it rerender.
A few extra pages may be prerendered at lower priority, so pageComplete may be called for pages that are not currently visibie. You can set the prerender level with the SetPreRenderLevel function.
You can subscribe to this event similar to how you subscribe to the documentLoaded event (as seen in the previous section).
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Remember that this callback is fired for every page on every document that is loaded. You can unsubscribe using the off function (as seen in the previous section).
DocumentViewer.annotationsLoaded
This event is fired when all the annotations have been loaded into memory. At this point you can start interacting with the annotations, such as saving and loading .
We load annotations asyncronously in the background, and they may be rendered before this event is fired.
You can subscribe to the event like so:
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Input events
These input events are fired when the mouse and keyboard are interacting with the document viewer.
Here is an example of an onHover for annotations using the mouseMove event.
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+)
Did you find this helpful?
Trial setup questions?
Ask experts on DiscordNeed other help?
Contact SupportPricing or product questions?
Contact Sales