Product:
Get started with Apryse WebViewer SDK in an Electron Project
The WebViewer SDK base package is robust, allowing you to do the following with PDFs inside your app:
- View
- Annotate
- Flatten
- Extract
- Search
- Build forms
- Calculate using measurements
- Support layers
- Customize the UI
- Meet global accessibility standards through the UI
You can also take advantage of our add-on packages for further capabilities.
Adding WebViewer to your application allows users to use PDFs without going outside of your application. This reduces reliance on third-party systems, multiple vendors, and file downloads for everyday tasks without compromising control, compliance, or security.
Interact with our showcase demo to test out all of the Apryse WebViewer SDK functionality.
This guide walks you through how to integrate the WebViewer SDK into an electron application . By the end, you'll be able to render a PDF document in the UI.
You can also download a ready-to-go sample on GitHub.
Prerequisites
Prior to starting, you should:
- Install Node and npm to use as your run-time environment and package manager.
- Open a text editor like Visual Studio Code.
- Get your Apryse trial key.
License Key
Apryse collects some data regarding your usage of the SDK for product improvement.
If you wish to continue without data collection, contact us and we will email you a no-tracking trial key for you to get started.
Get started video
Get started with the Apryse WebViewer SDK in an Electron project by viewing our video. This video includes instructions for successfully integrating the WebViewer SDK into your application. You can also skip the video and, instead, follow the steps below to get started.
Integrate Apryse WebViewer into your Electron project
1. Create project directory
If you already have an Electron app, skip to Section 5 below.
Create your Electron project.
1. On the command line, cd to where you want your new project to sit.
2. Run the following on the command line to generate your project, replacing <projectName> with the name of your project:
Use camel case when naming your new project. Characters like dashes and underscores in the project name won't work when you run npm init as a next step later.
The npm init command is used to create a package.json file in the current directory, which is essential for any Node.js project or npm package. This file acts as a manifest for your project, storing important metadata and configuration information.
shell
2. Navigate to new Electron project
Enter the following on the command line to navigate into your new project, replacing <projectName> with the name of your project:
shell
3. Initialize project
- Enter the following command on the command line from your new project directory to create a
package.jsonfile within your project:
shell
2. Next, click Enter on your keyboard.
3. Enter configurations for your project on the command line. You may enter any values with one exception:
- For the
entry pointoption, entermain.js.
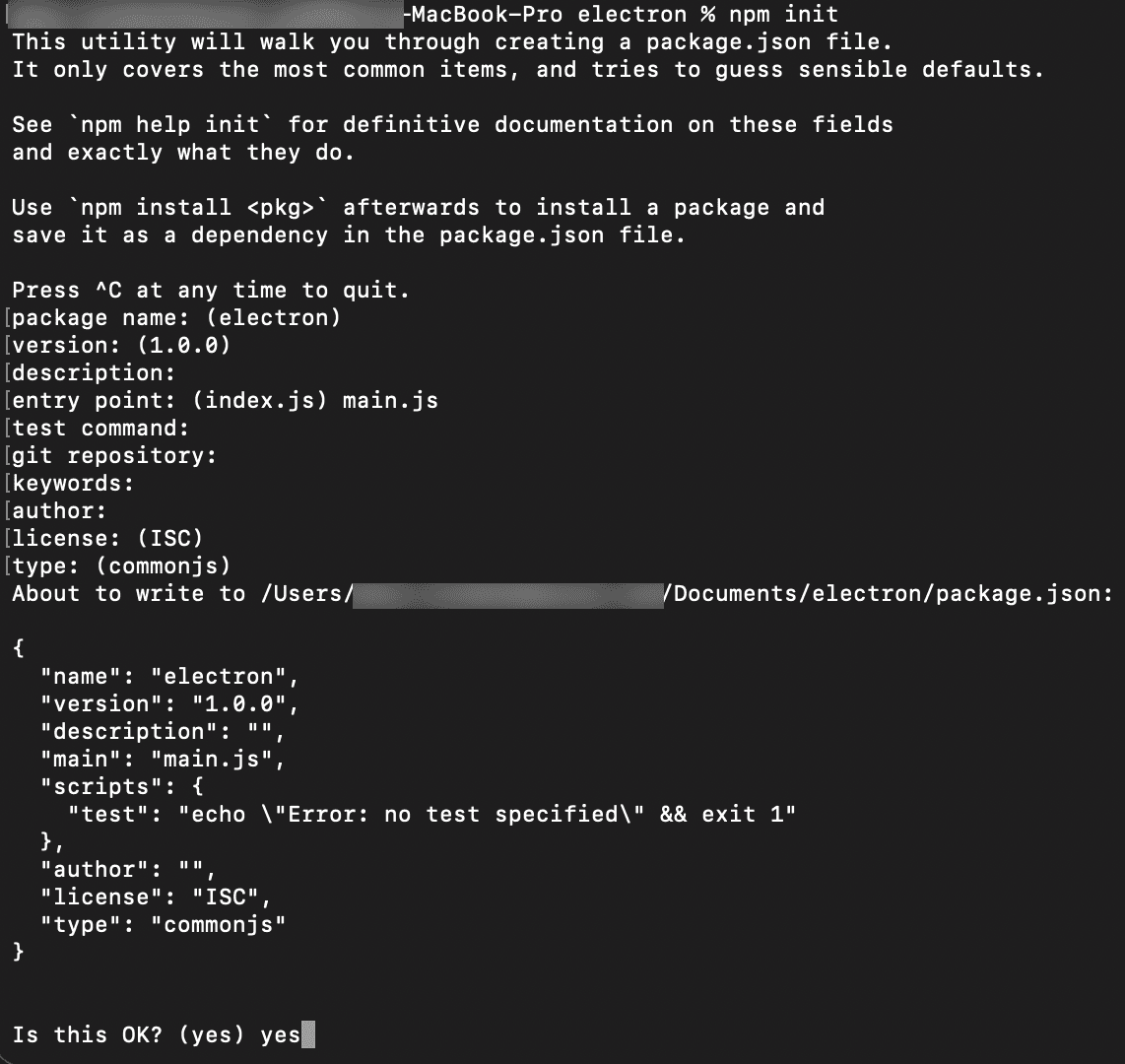
Configuration options on command line when you initialize the project
After answering all the questions, you should have a package.json file in the folder you created.
4. Install Electron
Install Electron from the command line within your new project:
shell
5. Install WebViewer
From your project directory on the command line, install WebViewer into your project:
shell
6. Add start script and copy static assets
In addition to installing WebViewer, you need to:
- Set up a script to start Electron.
- set up a script to copy the static WebViewer dependencies into a statically served folder in your project. The reason for this is because WebViewer contains many assets that cannot be bundled by the build system. Instead, these assets need to be served statically.
In package.json, add the following commands that start Electron and copy the static assets to a lib/webviewer folder.
JSON
Read more about copying WebViewer static assets.
Your package.json file should now look similar to the following:
JSON
7. Implement WebViewer
Implement WebViewer into your project.
a. Create html file
- Create an
index.htmlfile within your project. It will be used to render your app.
2. Add the following code to the new file:
HTML
index.html
b. Import WebViewer and create container
Next, you'll import the WebViewer library and create a DOM element for it to mount to.
1. In the <head> block of your index.html file, add the following code:
HTML
2. In the <body>of the index.html file, add the following code:
HTML
The code creates an empty div with the ID viewer.
c. Load the html file with Electron
1. Create a new file in your project named main.js. This Javascript file will be used to run your application.
2. In the main.js file, add the following code:
This code will load the HTML file.
JavaScript
main.js
d. Initialize WebViewer
Now, you're ready to initialize WebViewer. This needs to be done in a render process.
- Create a file named
render.js. - Add the following code to the new file, keeping the following in mind:
pathis the path to the copied static assets.- An initial PDF document is specified to open when WebViewer starts using the
initialDocparameter. - Add your own license key in place of 'YOUR_LICENSE_KEY'. If you've created your license key and you're logged in, your key is already in the code below.
JavaScript
render.js
3. Add the following code to the bottom of the <body> tag in the index.html file. This imports the renderer script.
HTML
index.html
6. View PDF in WebViewer UI
After you've saved all of the files, you'll serve the webpage so you can see the WebViewer UI and the PDF you included to open in WebViewer.
1. Run the following command on the command line from your project directory to run the project:
sh
2. Click the localhost link created in your terminal to view the WebViewer UI and PDF file locally.
Next steps
Check out the resources below.
Did you find this helpful?
Trial setup questions?
Ask experts on DiscordNeed other help?
Contact SupportPricing or product questions?
Contact Sales