Product:
Get Started with the Apryse WebViewer SDK in a Project Powered by Vite
The WebViewer SDK base package is robust, allowing you to do the following with PDFs inside your app:
- View
- Annotate
- Flatten
- Extract
- Search
- Build forms
- Calculate using measurements
- Support layers
- Customize the UI
- Meet global accessibility standards through the UI
You can also take advantage of our add-on packages for further capabilities.
Adding WebViewer to your application allows users to use PDFs without going outside of your application. This reduces reliance on third-party systems, multiple vendors, and file downloads for everyday tasks without compromising control, compliance, or security.
Interact with our showcase demo to test out all of the Apryse WebViewer SDK functionality.
This guide walks you through how to integrate the WebViewer SDK into a application powered by Vite. By the end, you'll be able to render a PDF document in the UI.
Prerequisites
Before you start:
- Install Node and npm to use as your run-time environment and package manager.
- Open a text editor like Visual Studio Code.
- Get your Apryse trial key.
License Key
Apryse collects some data regarding your usage of the SDK for product improvement.
If you wish to continue without data collection, contact us and we will email you a no-tracking trial key for you to get started.
Get started video
This video teaches you the fundamentals of installing and initializing the Apryse WebViewer SDK in any web application. If you wish, you may skip this section and proceed to the steps below.
Get started with Apryse Webviewer SDK
1. Scaffold project with Vite
First, you'll create your project.
Note
If you already have a project powered by Vite, skip to step 3.
1. On the command line, cd to where you want your new project to sit.
2. Run the following on the command line to use the Vite CLI to generate a project:
shell
3. Next, complete the following tasks from the command line during project creation:
a. Change the default Project name to a project name of your choice.
b. Select either React, Vanilla, Vue, or Svelte as your framework if you want to use our ready-made code samples later in this tutorial. You can, of course, select any framework and write your own code.
c. Select Javascript for your variant.
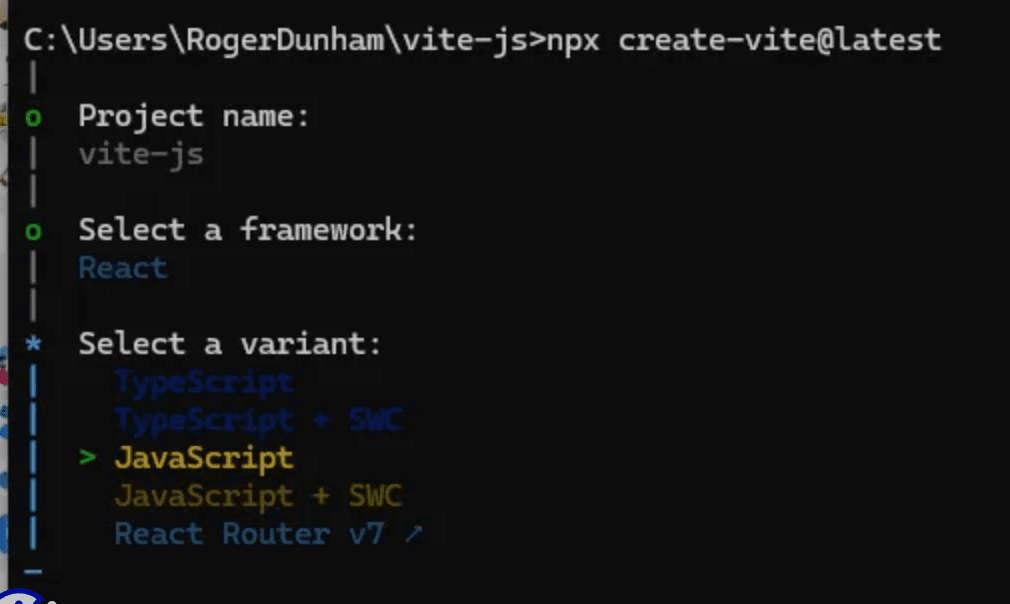
Options you must select during Vite project setup.
2. Navigate to new project
Enter the following on the command line to navigate into your new project, replacing <project-name> with the name you chose:
shell
3. Install Vite dependencies
Run the following command on the command line from within your project directory to install Vite dependencies:
shell
4. Integrate WebViewer
Next, you'll integrate WebViewer into your project.
Run the following command on the command line, from your project directory:
shell
5. Install Vite plugin
Next, you'll use a Vite plugin to copy WebViewer's static assets into a public folder in the project.
Run the following command on the command line within your project directory:
sh
You'll use this dependency no matter what framework you're using.
6. Copy static WebViewer assets
WebViewer comes with many static assets that can't be bundled directly by Vite. Instead, these static assets need to be served from the filesystem.
To do this, you'll copy these static WebViewer assets into the public folder created by Vite using the vite-plugin-static-copy plugin you installed earlier.
From your text editor, in the vite.config file, you'll add viteStaticCopy plugin to the plugins array like this (select the framework you're using from the tabs below since the code is framework specific):
JavaScript
JavaScript
JavaScript
JavaScript
Your config file might look slightly different, depending on what framework you're using. What's important is that you're adding the viteStaticCopy plugin to the plugins array.
No vite.config.js?
If you do not see a vite.config.js file in your project, you can create one under your main project folder via your text editor and add the following code:
JavaScript
7. Instantiate and mount WebViewer
Now, all of the configuration is done and you're ready to start using WebViewer.
Initialization varies depending on your framework, but, in general, the process is:
1. Import WebViewer.
2. Create a DOM element to mount WebViewer to.
3. Call the WebViewer constructor and provide the DOM element you want to mount it to and the path to your static WebViewer assets you copied in the previous step.
Below are some code samples of what this would look like in a few frameworks. Select the framework you need from the tabs below, then, from your text editor, add the code to the corresponding file.
JavaScript
App.jsx
JavaScript
App.css
If you were to run WebViewer in the browser now for your React project, a second WebViewer instance would display. This isn’t an issue with WebViewer. It's caused by recent versions of React. Prior to React v18, a useEffect with an empty dependency array would fire just a single time when the page loaded, and this was used to construct WebViewer.
However, since React v18, if StrictMode is specified (and Vite does so by default), then the useEffect fires a second time in Development builds. This isn’t an issue with Production builds though – so it’s an artificial problem.
A simple way to solve the problem in a Development build is to remove the StrictMode tags. We'll do that for this simple proof of concept.
Delete the StrictMode tags from the src/main.jsx file. Your file should look like this after the deletion:
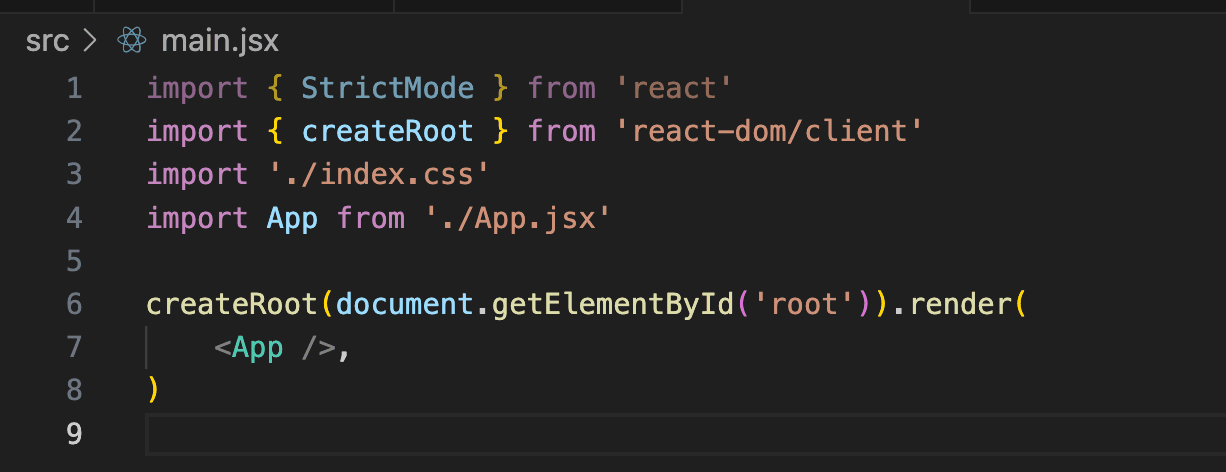
The main.jsx file after you've deleted the StrictMode tags
Removing StrictMode isn’t ideal. It was implemented as a way to find memory leaks. That might not be a problem in a proof of concept like this, but you would definitely care about in a more complex project. Read more about common workarounds.
JavaScript
main.js
JavaScript
components/HelloWorld.vue
JavaScript
lib/App.svelte
JavaScript
App.svelte
8. View PDF in WebViewer UI
After you've saved all of the files, you'll serve the webpage so you can see the WebViewer UI and the PDF you included to open in WebViewer.
1. Run the following command on the command line from your project directory to run the project.
sh
2. Click the localhost link created in your terminal to view the WebViewer UI and PDF file locally.
Clean up CSS
If you started from scratch and used the Vite scaffolding tool, the default CSS it ships with may interfere with the styles. If WebViewer doesn't display once you run the project, delete all the styles from any CSS files set up by Vite using your text editor.
Next steps
Did you find this helpful?
Trial setup questions?
Ask experts on DiscordNeed other help?
Contact SupportPricing or product questions?
Contact Sales