Requirements These packages are required to use these features in production. Trial keys have unlimited access to all features.
Adding text or an image as a watermark on top of a document requires only a few lines of code using the setWatermark
To draw a watermark, use documentViewer.setWatermark
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 WebViewer ({
2 initialDoc : ' https://url/to/my_file.docx ' ,
3 // ...
4 }, viewerElement)
5 . then ( instance => {
6 const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
7
8 documentViewer. setWatermark ({
9 // Draw diagonal watermark in middle of the document
10 diagonal : {
11 fontSize : 25 , // or even smaller size
12 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
13 color : ' red ' ,
14 opacity : 50 , // from 0 to 100
15 text : ' Watermark '
16 },
17
18 // Draw header watermark
19 header : {
20 fontSize : 10 ,
21 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
22 color : ' red ' ,
23 opacity : 70 ,
24 left : ' left watermark ' ,
25 center : ' center watermark ' ,
26 right : ''
27 }
28 });
29 });
1 WebViewer ({
2 initialDoc : ' https://url/to/my_file.docx ' ,
3 // ...
4 }, viewerElement)
5 . then ( instance => {
6 const { docViewer } = instance;
7 docViewer. setWatermark ({
8 // Draw diagonal watermark in middle of the document
9 diagonal : {
10 fontSize : 25 , // or even smaller size
11 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
12 color : ' red ' ,
13 opacity : 50 , // from 0 to 100
14 text : ' Watermark '
15 },
16 // Draw header watermark
17 header : {
18 fontSize : 10 ,
19 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
20 color : ' red ' ,
21 opacity : 70 ,
22 left : ' left watermark ' ,
23 center : ' center watermark ' ,
24 right : ''
25 }
26 });
27 });
The setWatermark
For the following sample, we will use a Promise which will resolve with the watermark options object. If the document hasn't been loaded yet then DocumentViewer will wait to finish loading it until the watermark options are ready.
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v7.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 WebViewer ({
2 initialDoc : ' https://url/to/my_file.docx ' ,
3 // ...
4 }, viewerElement)
5 . then ( instance => {
6 const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
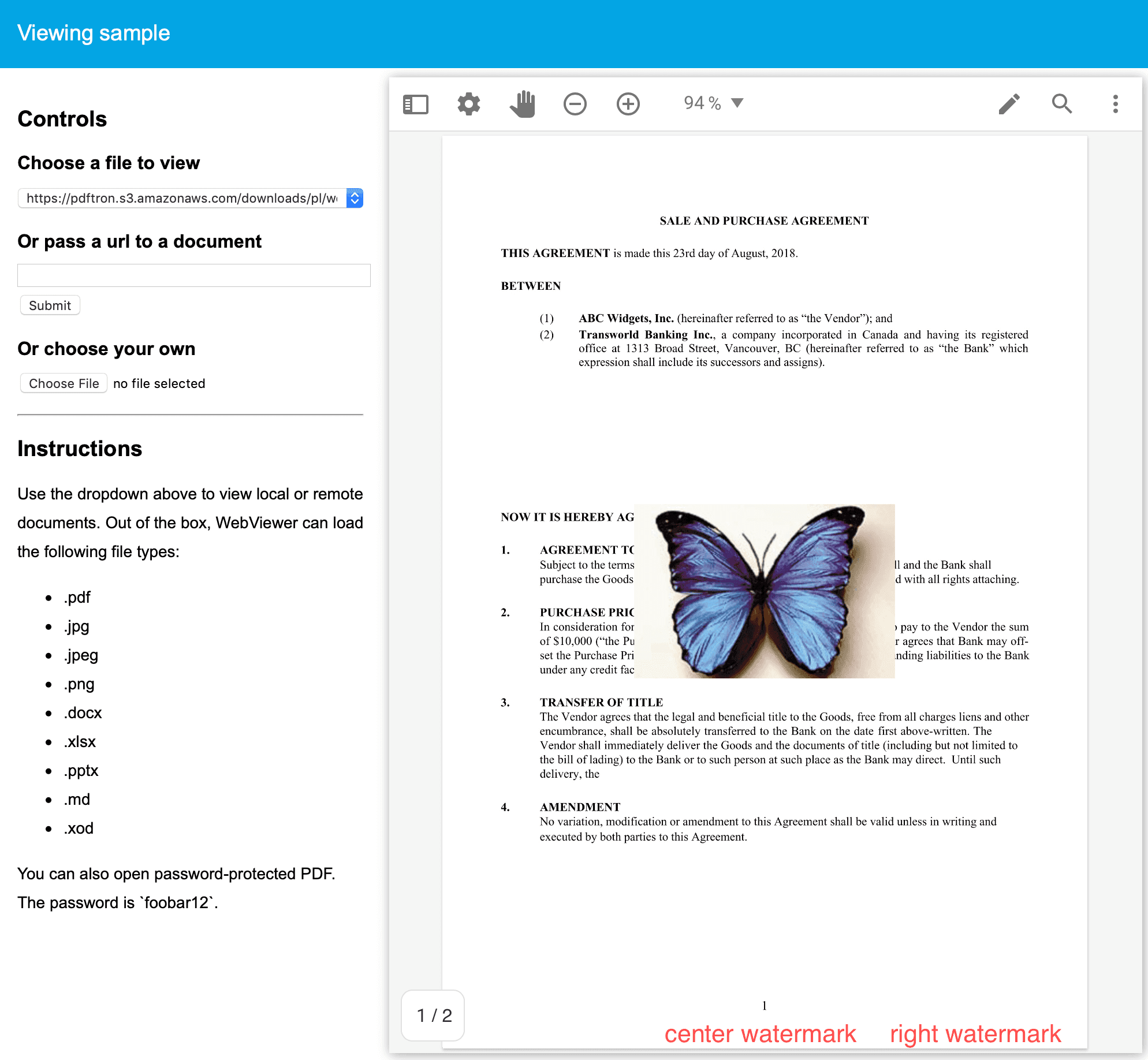
7 const path = ' /samples/full-apis/TestFiles/butterfly.png '
8 // Promise resolves with options object
9 const promise = new Promise ( resolve => {
10 const img = new Image ();
11 const options = {
12 footer : {
13 fontSize : 15 ,
14 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
15 color : ' red ' ,
16 opacity : 70 ,
17 left : ' left watermark ' ,
18 center : ' center watermark '
19 },
20 custom : ( ctx , pageNumber , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
21 // the pageNumber is also passed in so you could have
22 // a different watermark for each page
23 ctx. drawImage (
24 img,
25 pageWidth / 2 - img.width / 2 ,
26 pageHeight / 2 - img.height / 2
27 );
28 }
29 };
30 img. onload = () => {
31 return resolve (options);
32 };
33 img.src = path;
34 });
35 documentViewer. setWatermark (promise);
36 });
1 WebViewer ({
2 initialDoc : ' https://url/to/my_file.docx ' ,
3 // ...
4 }, viewerElement)
5 . then ( instance => {
6 const { docViewer } = instance;
7 const path = ' /samples/full-apis/TestFiles/butterfly.png '
8 // Promise resolves with options object
9 const promise = new Promise ( resolve => {
10 const img = new Image ();
11 const options = {
12 footer : {
13 fontSize : 15 ,
14 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
15 color : ' red ' ,
16 opacity : 70 ,
17 left : ' left watermark ' ,
18 center : ' center watermark '
19 },
20 custom : ( ctx , pageNumber , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
21 // the pageNumber is also passed in so you could have
22 // a different watermark for each page
23 ctx. drawImage (
24 img,
25 pageWidth / 2 - img.width / 2 ,
26 pageHeight / 2 - img.height / 2
27 );
28 }
29 };
30 img. onload = () => {
31 return resolve (options);
32 };
33 img.src = path;
34 });
35 docViewer. setWatermark (promise);
36 });
1 WebViewer ({
2 initialDoc : ' https://url/to/my_file.docx ' ,
3 // ...
4 }, viewerElement)
5 . then ( instance => {
6 const { docViewer } = instance;
7 const path = ' /samples/full-apis/TestFiles/butterfly.png '
8 // Promise resolves with options object
9 const promise = new Promise ( resolve => {
10 const img = new Image ();
11 const options = {
12 footer : {
13 fontSize : 15 ,
14 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
15 color : ' red ' ,
16 opacity : 70 ,
17 left : ' left watermark ' ,
18 center : ' center watermark '
19 },
20 custom : ( ctx , pageIndex , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
21 // the pageIndex is also passed in so you could have
22 // a different watermark for each page
23 ctx. drawImage (
24 img,
25 pageWidth / 2 - img.width / 2 ,
26 pageHeight / 2 - img.height / 2
27 );
28 }
29 };
30 img. onload = () => {
31 return resolve (options);
32 };
33 img.src = path;
34 });
35 docViewer. setWatermark (promise);
36 });
The setWatermark custom
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v7.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 WebViewer ({
2 // ...
3 }, viewerElement)
4 . then ( instance => {
5 const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
6 documentViewer. setWatermark ({
7 custom : ( ctx , pageNumber , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
8 // ctx is an instance of CanvasRenderingContext2D
9 // https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/CanvasRenderingContext2D
10 // Hence being able to leverage those properties
11 ctx.fillStyle = ' #ff0000 ' ;
12 ctx.font = ' 20pt Arial ' ;
13 ctx.globalAlpha = 0.4 ;
14
15 ctx. save ();
16 ctx. translate ( 0 , pageHeight / 2 );
17 ctx. rotate ( - Math. PI / 2 );
18 ctx. fillText ( ' left side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
19 ctx. restore ();
20
21 ctx. save ();
22 ctx. translate (pageWidth, pageHeight / 2 );
23 ctx. rotate (Math. PI / 2 );
24 ctx. fillText ( ' right side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
25 ctx. restore ();
26 },
27 });
28 });
1 WebViewer ({
2 // ...
3 }, viewerElement)
4 . then ( instance => {
5 const { docViewer } = instance;
6 docViewer. setWatermark ({
7 custom : ( ctx , pageNumber , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
8 // ctx is an instance of CanvasRenderingContext2D
9 // https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/CanvasRenderingContext2D
10 // Hence being able to leverage those properties
11 ctx.fillStyle = ' #ff0000 ' ;
12 ctx.font = ' 20pt Arial ' ;
13 ctx.globalAlpha = 0.4 ;
14
15 ctx. save ();
16 ctx. translate ( 0 , pageHeight / 2 );
17 ctx. rotate ( - Math. PI / 2 );
18 ctx. fillText ( ' left side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
19 ctx. restore ();
20
21 ctx. save ();
22 ctx. translate (pageWidth, pageHeight / 2 );
23 ctx. rotate (Math. PI / 2 );
24 ctx. fillText ( ' right side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
25 ctx. restore ();
26 },
27 });
28 });
1 WebViewer ({
2 // ...
3 }, viewerElement)
4 . then ( instance => {
5 const { docViewer } = instance;
6 docViewer. setWatermark ({
7 custom : ( ctx , pageIndex , pageWidth , pageHeight ) => {
8 // ctx is an instance of CanvasRenderingContext2D
9 // https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/CanvasRenderingContext2D
10 // Hence being able to leverage those properties
11 ctx.fillStyle = ' #ff0000 ' ;
12 ctx.font = ' 20pt Arial ' ;
13 ctx.globalAlpha = 0.4 ;
14
15 ctx. save ();
16 ctx. translate ( 0 , pageHeight / 2 );
17 ctx. rotate ( - Math. PI / 2 );
18 ctx. fillText ( ' left side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
19 ctx. restore ();
20
21 ctx. save ();
22 ctx. translate (pageWidth, pageHeight / 2 );
23 ctx. rotate (Math. PI / 2 );
24 ctx. fillText ( ' right side watermark ' , 0 , 0 );
25 ctx. restore ();
26 },
27 });
28 });
If you're constructing your own Document instance then it also provides a setWatermark
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 const filePath = ' /webviewer-demo.pdf ' ;
2 const watermarkOptions = {
3 header : {
4 fontSize : 15 ,
5 color : ' blue ' ,
6 center : ' center watermark ' ,
7 },
8 diagonal : {
9 fontSize : 30 ,
10 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
11 color : ' red ' ,
12 opacity : 100 ,
13 text : ' Watermark '
14 }
15 };
16 const doc = await Core. createDocument (filePath, { l : ' YOUR_LICENSE_KEY ' });
17 // Set watermark options object
18 doc. setWatermark (watermarkOptions);
19 // Draw canvas
20 doc. loadCanvasAsync ({
21 pageIndex : 0 ,
22 getZoom : () => 0.8 , // 80% zoom,
23 drawComplete : pageCanvas => {
24 // Append canvas to dom to see the result
25 document.body. appendChild (pageCanvas);
26 },
27 });
1 const filePath = ' /webviewer-demo.pdf ' ;
2 const watermarkOptions = {
3 header : {
4 fontSize : 15 ,
5 color : ' blue ' ,
6 center : ' center watermark ' ,
7 },
8 diagonal : {
9 fontSize : 30 ,
10 fontFamily : ' sans-serif ' ,
11 color : ' red ' ,
12 opacity : 100 ,
13 text : ' Watermark '
14 }
15 };
16 const doc = await CoreControls. createDocument (filePath, { l : ' YOUR_LICENSE_KEY ' });
17 // Set watermark options object
18 doc. setWatermark (watermarkOptions);
19 // Draw canvas
20 doc. loadCanvasAsync ({
21 pageIndex : 0 ,
22 getZoom : () => 0.8 , // 80% zoom,
23 drawComplete : pageCanvas => {
24 // Append canvas to dom to see the result
25 document.body. appendChild (pageCanvas);
26 },
27 });
If you want to add a watermark or modify the existing watermark after pages are rendered, then after calling setWatermarkrefreshAllupdateView
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 WebViewer ( ... )
2 . then ( instance => {
3 const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
4 const watermarkOptions = { ... };
5 documentViewer. setWatermark (watermarkOptions);
6 documentViewer. refreshAll ();
7 documentViewer. updateView ();
8 })
1 WebViewer ( ... )
2 . then ( instance => {
3 const { docViewer } = instance;
4 const watermarkOptions = { ... };
5 docViewer. setWatermark (watermarkOptions);
6 docViewer. refreshAll ();
7 docViewer. updateView ();
8 })
If you are going to use a Promise then you need to call those two methods after the Promise has resolved:
JavaScript (SDK v8.0+) JavaScript (SDK v6.0+)
1 WebViewer ( ... )
2 . then ( instance => {
3 const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
4 const promise = new Promise ( resolve => {
5 // some asynchronous operations to generate the watermark options object
6 resolve (watermarkOptions);
7 });
8 documentViewer. setWatermark (promise);
9 documentViewer. getWatermark (). then (() => {
10 documentViewer. refreshAll ();
11 documentViewer. updateView ();
12 })
13 })
1 WebViewer ( ... )
2 . then ( instance => {
3 const { docViewer } = instance;
4 const promise = new Promise ( resolve => {
5 // some asynchronous operations to generate the watermark options object
6 resolve (watermarkOptions);
7 });
8 docViewer. setWatermark (promise);
9 docViewer. getWatermark (). then (() => {
10 docViewer. refreshAll ();
11 docViewer. updateView ();
12 })
13 })
The WebViewer SDK includes a setWatermarkRenderQuality(multiplier) API to provide finer control over how watermarks are rendered when using the setWatermarkembedded printing , where rasterization artifacts can occur.
This API allows you to adjust the rasterization multiplier used during watermark rendering. By increasing the multiplier, you can enhance the output quality of the watermark, which can reduce pixelation or blurriness.
You can call this API from either the DocumentViewer or Document namespaces. To apply the quality setting globally to all documents in your app, call it from the DocumentViewer. If you only want to apply it to a specific document, call it directly on that document instance.
JavaScript 1 // Calling from Document Viewer
2 await instance.Core.documentViewer. setWatermarkRenderQuality ( 4 );
3
4 // Calling from a Document
5 const documentViewer = instance.Core.documentViewer;
6 const doc = documentViewer. getDocument ();
7 await doc. setWatermarkRenderQuality ( 3 );